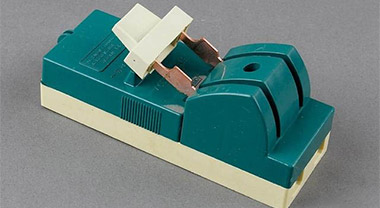
Working principle of molded case circuit breaker
What is a molded case circuit breaker?
Molded case circuit breakers are generally suitable for the interface between the 400V power supply of the power supply system and the low-voltage power distribution system. They are widely used in the secondary load small power distribution box and the tertiary load small power power distribution box in subway stations. , Dual power switch box, fire control cabinet and MCC cabinet system; part of the low-voltage power distribution system of the depot and section also uses molded case circuit breakers. The types of circuit breakers used in the low-voltage power distribution system of subway stations are generally VL160, VL250, etc., indicating that the rated current is 160A, 250A.

Working principle of molded case circuit breaker
The main contacts of low-voltage circuit breakers are manually operated or electrically closed. After the main contact is closed, the free trip mechanism locks the main contact in the closed position. The coil of the overcurrent release and the thermal element of the thermal release are connected in series with the main circuit, and the coil of the undervoltage release is connected in parallel with the power supply.
When the circuit is short-circuited or severely overloaded, the armature of the overcurrent release pulls in, causing the free tripping mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit.
When the circuit is overloaded, the thermal element of the thermal trip unit generates heat to bend the bimetallic strip, pushing the free trip mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit.
When the circuit is under-voltage, the armature of the under-voltage release is released, and the free trip mechanism is also activated, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit.
When the shunt trip button is pressed, the armature of the shunt trip unit pulls in, causing the free trip mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit.
The main parameters of plastic case circuit breaker
1. Rated voltage
The rated voltage on the nameplate of the circuit breaker refers to the rated voltage of the main contact of the circuit breaker, and is the voltage value that guarantees the long-term normal operation of the contactor of the contactor.
2. Rated current
The rated current on the nameplate of the contactor refers to the rated current of the main contact of the router, and is the current value that guarantees the long-term normal operation of the contactor.
3. Tripping current
The trip current is the current setting value that causes the overcurrent release to operate. When the circuit is short-circuited or the load is seriously overloaded, and the load current is greater than the trip current, the main contact of the circuit breaker is broken.
4. Overload protection current and time curve
The overload protection current and time curve are inverse time characteristic curves. The larger the overload current, the shorter the time for the thermal release to act.
5. The rated voltage of the undervoltage release coil
The rated voltage of the undervoltage release coil must be equal to the rated voltage of the line.
6. Rated voltage of the shunt release coil
The rated voltage of the shunt release coil must be equal to the control power supply voltage.
7. Rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity Icu
There are two kinds of breaking capacity indexes of circuit breakers: rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity Icu and rated operating short-circuit breaking capacity Ics.
The rated limit short-circuit breaking capacity Icu is the limit parameter of the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker. After several short-circuit faults are broken, the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker will decrease.
The rated operating short-circuit breaking capacity Ics is a breaking index of the circuit breaker, that is, after breaking several short-circuit faults, the normal operation can be guaranteed.
For molded case circuit breakers, as long as Ics is greater than 25% Icu, it is considered qualified. At present, most of the Ics of circuit breakers on the market are between (50%-75%) Icu.
8. Current limiting and breaking capacity
Current-limiting and breaking capacity refers to the ability to limit the fault current when the circuit breaker trips when the circuit is short-circuited. When the circuit is short-circuited, the contacts of the circuit breaker open rapidly and an arc is generated, which is equivalent to inserting a rapidly increasing arc resistance in the line, which limits the increase of fault current and reduces the electromagnetic, electrical and thermal effects of the short-circuit current. Adverse effects on circuit breakers and electrical equipment, prolong the service life of circuit breakers. The shorter the breaker opening time, the better the current limiting effect, and the closer Ics is to Icu.