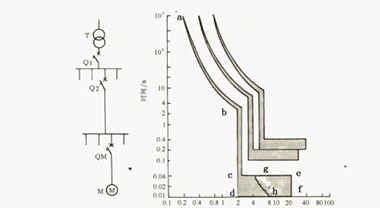
Inter-stage coordination of low-voltage circuit breaker selection
When the circuit breaker is used as the protection of the upper and lower levels, its action should be selective, and all levels should coordinate with each other. The selective coordination between the upper and lower stages of the circuit breaker must have "selectivity, rapidity and sensitivity". The selectivity is related to the coordination between the upper and lower circuit breakers, and the speed and sensitivity are respectively related to the characteristics of the circuit breaker and the line operation mode. You can refer to the upper and lower circuit breaker coordination selection table provided by the manufacturer for setting. If the upper and lower circuit breakers are matched properly, the faulty circuit can be selectively cut off to ensure that other fault-free circuits of the power distribution system continue to work normally, otherwise it will affect the reliability of the power distribution system. Cascading protection is a specific application of the current-limiting characteristics of circuit breakers. Its main principle is to use the current-limiting effect of the upper-level circuit breaker to reduce its breaking capacity when selecting the lower-level circuit breaker, which is reliable in protection and reduces costs. When selecting a circuit breaker, attention should be paid to the verification of its sensitivity. For selective circuit breakers with both short delay and instantaneous tripping, only the operating sensitivity of the short delay overcurrent release needs to be verified. Check the sensitivity of the instantaneous overcurrent release. When the circuit breaker is used as a short-circuit protection, the short-circuit current of the circuit should not be less than 1.3 times of the setting current of the instantaneous or short-delay overcurrent release to meet the sensitivity requirements to ensure the reliable operation of the circuit breaker. In order to make the circuit breaker reliably cut off the ground fault circuit, the requirements for ground fault protection are also different for different grounding types and use of electrical equipment. For the TN system, when the overcurrent protection can meet the requirement to cut off the ground fault line within the specified time, the overcurrent protection should also be used as the ground fault protection; in the three-phase four-wire distribution line, when the overcurrent protection cannot When the ground fault line is cut off within the specified time and the zero-sequence current protection can be satisfied, the zero-sequence current protection should be adopted, but the protection setting value should be greater than the maximum unbalanced current of the distribution line; when the above two protections cannot meet the requirements , The residual current operated circuit breaker should be used.
The current intelligent circuit breakers generally have the function of zone selective interlocking (ZSI), and use microelectronic technology to make the protection more perfect. They are mainly divided into short-circuit fault interlock and ground fault interlock, which play an important role in the hierarchical power distribution system. The function of the circuit breaker can solve the problem of coordination between the circuit breakers and ensure the sensitivity and selectivity of the action.
Matters needing attention in coordination between upper and lower levels
When the circuit breaker is used as upper and lower protection, its action should be selective, and the upper and lower levels should cooperate with each other, and pay attention to the following issues:
1) When the upper and lower actions of the circuit breaker are selective, attention should be paid to the matching of the current release setting value and time. Generally, the setting current of the upper circuit breaker for overload long delay and short circuit short delay should not be less than that of the lower circuit breaker. 1.3 times the value to ensure the action selectivity between the upper and lower levels. Under normal circumstances, the first-level circuit breaker (such as the low-voltage side of the transformer) should use the protection characteristics of overload long delay, short circuit short delay (0~0.5 s delay adjustable), and no short-circuit instantaneous release. The second-level circuit breaker should choose overload long delay, short circuit short delay, short circuit instantaneous and ground fault protection. The bus tie breaker should be equipped with long-time overload protection and short-circuit short-time protection. There should be a difference time between the first and second short-circuit delays, which should not be less than 0.2 s.
2) When the upper stage is a selective circuit breaker and the next stage is a non-selective circuit breaker, the setting current of the short-circuit short-delay release of the upper-level circuit breaker should not be less than the setting current of the short-circuit instantaneous release of the lower-level circuit breaker 1.3 times of the current; the setting current of the instantaneous release of the upper-level circuit breaker should be greater than 1.2 times of the single-phase short-circuit current at the outlet end of the lower-level circuit breaker.
3) When both the upper and lower levels are non-selective circuit breakers, the level difference between the tripping devices of the upper and lower circuit breakers should be increased. The setting current of the long-delay release of the upper-level circuit breaker should not be less than twice the setting current of the long-delay release of the lower-level circuit breaker; the setting current of the instantaneous release of the upper-level circuit breaker should not be less than the setting current of the instantaneous release of the lower-level circuit breaker 1.4 times.
4) When the short-circuit current at the outlet of the lower-level circuit breaker is greater than the instantaneous release setting current of the upper-level circuit breaker, the lower-level circuit breaker should use a current-limiting circuit breaker to ensure the selectivity requirements.
5) When the distance between the upper and lower circuit breakers is very close, and the expected short-circuit current difference between the outlet ends is very small, the upper circuit breaker should be equipped with a short-delay release to delay the action to ensure selective coordination.
6) The setting of the trip unit and time limit of the circuit breaker can generally refer to the following principles: The setting current of the long-time trip unit can be 0.9 to 1.1 times the rated current Ie of the trip unit, and the time limit can be selected as 15 s. The setting current of the short-delay release can be selected at 3 to 5 times the rated current Ie of the release, and the time limit can be selected at 0.1 s, 0.2 s and 0.4 s. The instantaneous release setting current can be selected as 10-15 times the rated current Ie of the release.